The importance of vaccinations and immunizations cannot be overstated in today's world. While many people are familiar with common vaccines, such as those for the flu or COVID-19, there are other critical vaccinations that often go unnoticed. One such example is the hepatitis B vaccine, which plays a crucial role in preventing a serious viral liver infection.
The hepatitis B vaccine is a key component of public health strategies aimed at eradicating this preventable disease. Hepatitis B is a viral infection that primarily affects the liver and can be transmitted through direct contact with infected blood or other bodily fluids, including sexual contact. It is important to clarify that while hepatitis B can indeed be sexually transmitted, it is not the sole means of transmission, which is why vaccination for newborns is essential .
Unvaccinated newborns are at risk of contracting the virus from their mothers or other family members. Given that the virus can cause lifelong liver damage, including cancer, and that most acute infections in children can last for up to 6 months, universal vaccination is paramount. The hepatitis B vaccine remains the most effective means of protection, providing long-term immunity. The vaccine is safe and effective, with various formulations including Engerix, Recombivax, and Heplisav-B .
The CDC's Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) is scheduled to discuss the vaccination schedule and recommendations for the hepatitis B vaccine this week. This committee plays a critical role in shaping the nation's vaccination policies, ensuring that they are backed by the latest scientific evidence and data .
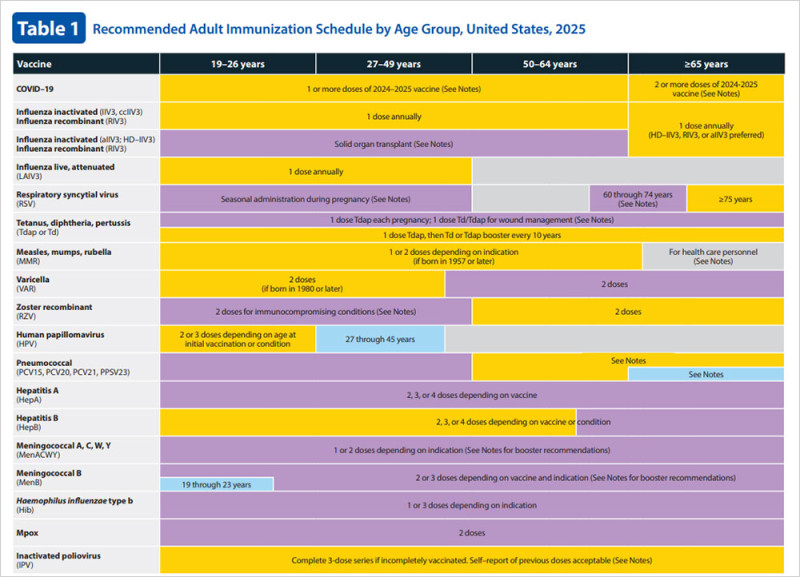
The hepatitis B vaccine is typically administered in a series of 2, 3, or 4 shots, with the first dose recommended at birth. Infants usually complete the vaccination series between 6 and 18 months of age. This early vaccination is essential for preventing long-term illness and the spread of hepatitis B in the United States .
ACIP's recommendations aim to ensure that everyone from infancy to 59 years of age receives the hepatitis B vaccine. For adults over 60, vaccination is recommended only if they have specific risk factors for contracting the virus. The universal vaccination policy underscores the importance of protecting individuals from a disease that can have lifelong consequences .
Public health officials emphasize that the hepatitis B vaccine is a safe and effective tool in the fight against this viral infection. With the continued support of organizations like the CDC and the ongoing advancements in vaccination science, we can look forward to a future where hepatitis B is significantly reduced, if not eradicated. Staying informed about the latest developments in vaccinations and immunizations is essential for maintaining a healthy and disease-free community .